Global PDF-based Non-local Means Filter
Introduction
Global PDF-based non-local means filter (GPDF) is a data-driven approach for filtering fMRI signals based on the probablity density functions (PDFs) of the correlations between time series. It allows users to perform a global filtering (enhanced distal and/or inter-hemispherical connections) with improved noise reduction effects but without blurring the boundaries between adjacent but distinct functional regions.
This page provides a MATLAB implementation of the GPDF filter described in
J. Li, S. Choi, A. A. Joshi, J. L. Wisnowski, R. M. Leahy, “Temporal non-local means filtering for studies of intrinsic brain connectivity from individual resting fMRI”, Medical Image Analysis, vol. 61, p. 101635, 2020.
J. Li, S. Choi, A. A. Joshi, J. L. Wisnowski, R. M. Leahy, “Global PDF-based temporal non-local means filtering reveals individual differences in brain connectivity”, IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washington D.C., Apr. 2018, pp. 15–19.
Please cite the papers above in your publications if you have used the GPDF filter in your research.
BrainSuite Integration
GPDF has been included as the default filtering method for fMRI data in the BrainSuite fMRI Processing (BFP) pipeline, which is released as part of the BrainSuite software.
“BrainSuite is a collection of image analysis tools designed to process magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the human head. BrainSuite provides an automatic sequence to extract cortical surface mesh models from the MRI, tools to register these to a labeled atlas to define anatomical regions of interest, and tools for processing diffusion imaging data. BrainSuite also contains visualization tools for exploring these data, and can produce interactive maps of regional connectivity.”
— BrainSuite
Example
The following figures show the filtering effects of Gaussian and GPDF, compared with the unfiltered case as a baseline. The either filtered or unfiltered individual resting fMRI data (HCP minimally processed) were played back in real time. Spatial patterns are barely visible if no filter is applied at all. Both Gaussian and GPDF filters can reduce the noise level, which reveals the spatial patterns (at least the default mode network is clearly identifiable). However, in the Gaussian case, the boundaries between different function regions (white) wobble a lot due to the spatial blurring of the Gaussian filter, while GPDF keeps the boundaries sharp.
| Unfiltered | Gaussian Filter | GPDF Filter |
|---|---|---|
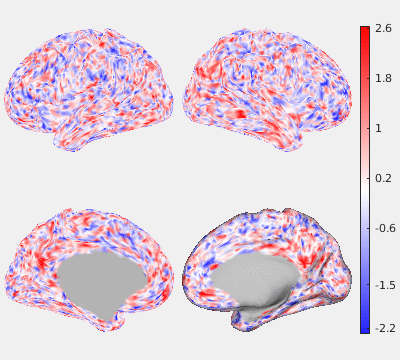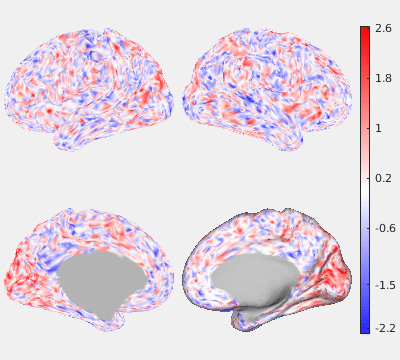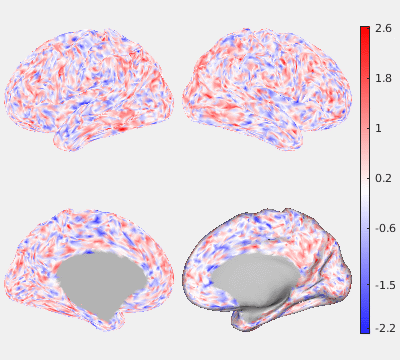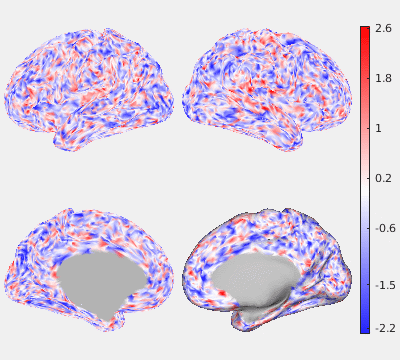 | 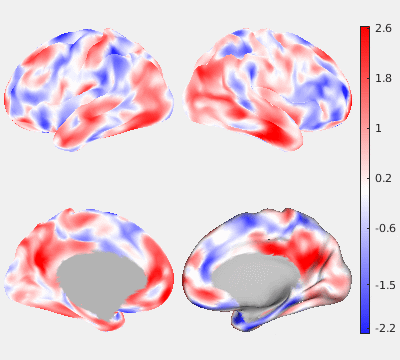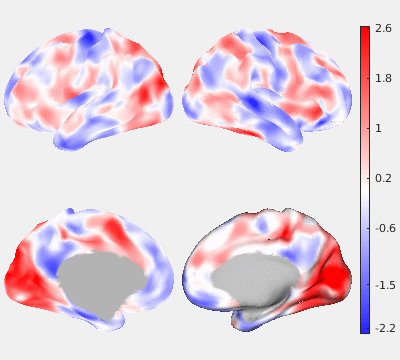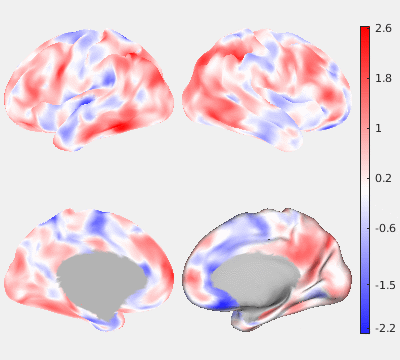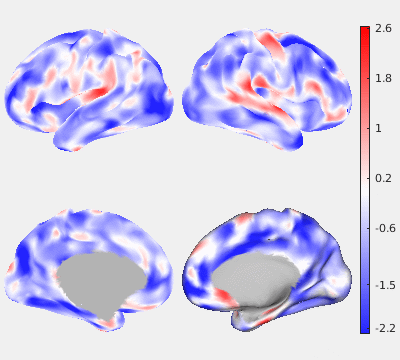 | 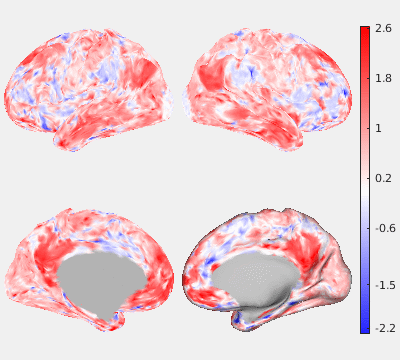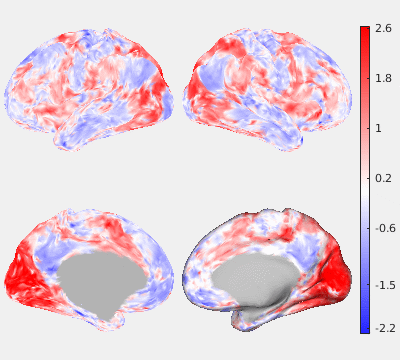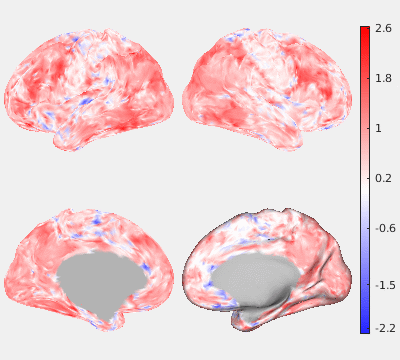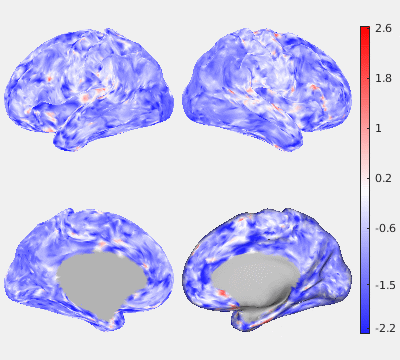 |
Disclaimer
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS, THE CONTRIBUTORS, THE DISTRIBUTORS AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA (“AUTHORS”) BE LIABLE TO ANY PARTY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING LOST PROFITS, ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF THIS CODE, EVEN IF THE AUTHORS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. THE AUTHORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. FOR RESEARCH PURPOSE ONLY. THIS CODE IS PROVIDED ON A “AS IS” BASIS AND THE AUTHORS HAVE NO OBLIGATION TO PROVIDE MAINTENANCE, SUPPORT, UPDATES, ENHANCEMENTS, OR MODIFICATIONS.
Download
Please follow this link (will open a new page) and fill out the form. An e-mail will be sent to you with a personal download link.