Scalable and Robust Sequential Canonical Polyadic Decomposition
Introduction
Tensor decompositions is a generalization of matrix decompostions in three or higher-dimensional space. One of the most widely used model is the canonical polyadic (CP) form, also known as parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) or canonical decomposition (CANDECOMP). Unlike applying the independent component analysis (ICA) or the principal component analysis (PCA) on the matricized / unfolded data for brain network identification, the CP decomposition can capture the low rank struture inherit in the higher-dimensional data. Moreover, it does not need to impose any constraint (in order to have a unique solution), such as independence in ICA or orthogonality in PCA, which may not be realistic as brain networks can overlap and be correlated in both space and time.
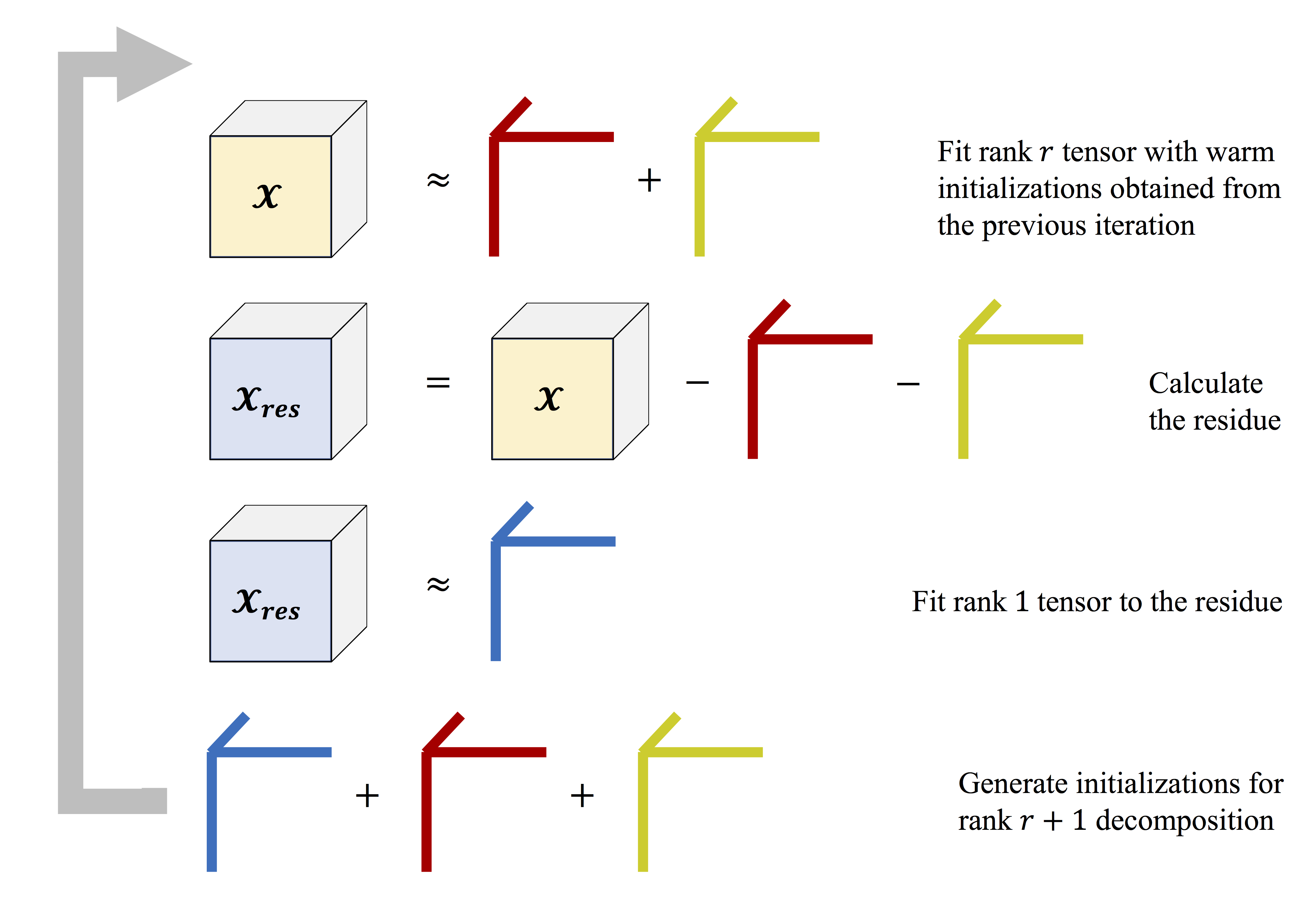
Scalable and Robust Sequential Canonical Polyadic Decomposition (SRSCPD) is a framework that offers robust solutions to CP decomposition problems and is scalable to large dataset. The scalability and robustness are achieved by using the lower rank solutions as part of the warm initializations for current rank decomposition. See illustration below.
This page provides a MATLAB implementation of SRSPCD described in
J. Li, J. P. Haldar, J. C. Mosher, D. R. Nair, J. Gonzalez-Martinez, R. M. Leahy, “Scalable and robust tensor decomposition of spontaneous stereotactic EEG data”, IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 66, no. 6, pp. 1549–1558, 2019.
J. Li, J. C. Mosher, D. R. Nair, J. Gonzalez-Martinez, R. M. Leahy, “Robust tensor decomposition of resting brain networks in stereotactic EEG”, IEEE 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, Oct. 2017, pp. 1544–1548.
Please cite the papers above in your publications if you have used SRSCPD in your research.
Graphical Illustration
Here is a graphical illustration of the SRSCPD framework. This framework is flexible in the sense that any CP decomposition algorithm, e.g., the alternating least square (ALS), can be used internally to solve each individual CP decomposition problem.
Disclaimer
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS, THE CONTRIBUTORS, THE DISTRIBUTORS AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA (“AUTHORS”) BE LIABLE TO ANY PARTY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING LOST PROFITS, ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF THIS CODE, EVEN IF THE AUTHORS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. THE AUTHORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. FOR RESEARCH PURPOSE ONLY. THIS CODE IS PROVIDED ON A “AS IS” BASIS AND THE AUTHORS HAVE NO OBLIGATION TO PROVIDE MAINTENANCE, SUPPORT, UPDATES, ENHANCEMENTS, OR MODIFICATIONS.
Download
Please follow this link (will open a new page) and fill out the form. An e-mail will be sent to you with a personal download link.